Analysis of Motion Blurred Images
This page discusses several papers related to the analysis of motion blurred images (i.e. my PhD thesis work).
On the Apparent Transparency of a Motion Blurred Object: extracting information from blurred smears
Vincenzo Caglioti, Alessandro Giusti
International Journal on Computer Vision, 2010
Abstract
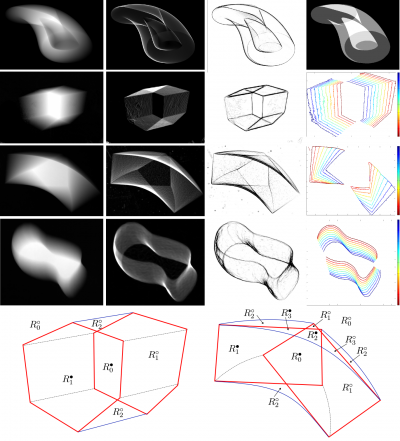
An object which moves during the exposure time results in a blurred smear in the image. We consider the smear as if it was the image of a semitransparent object, and we retrieve its alpha matte by means of known techniques. The alpha value at a pixel is meaningfully interpreted as the fraction of the exposure time during which the object projection overlapped that pixel. Basing on this fact, our work highlights interesting qualitative and quantitative properties of the alpha matte, which can be used to derive constraints on the object’s apparent contour, and its motion during the exposure time, from a single motion-blurred image; we also show that some of these properties hold on the original image. The theory is validated with experimental results both on synthetic and real images, highlighting strengths and limitations; we point out a range of possible applications, including blurred image interpretation, temporal superresolution of object contours, model-based reconstruction of nontrivial motion, and improvements of alpha matting techniques.
Paper
Bibtex
@article{caglioti2010apparent,
title={On the apparent transparency of a motion blurred object},
author={Caglioti, Vincenzo and Giusti, Alessandro},
journal={International journal of computer vision},
volume={86},
number={2-3},
pages={243--255},
year={2010},
publisher={Springer}
}
@inproceedings{giusti2007apparent,
title={On the apparent transparency of a motion blurred object},
author={Giusti, Alessandro and Caglioti, Vincenzo},
booktitle={Proceedings of the First International Workshop on Photometric Analysis For Computer Vision (PACV)},
year={2007}
}
Recovering ball motion from a single motion-blurred image
Vincenzo Caglioti, Alessandro Giusti
Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2008
Abstract
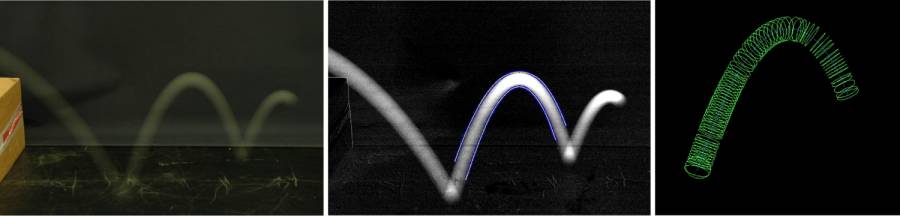
Motion blur often affects the ball image in photographs and video frames in many sports such as tennis, table tennis, squash and golf. In this work, we operate on a single calibrated image depicting a moving ball over a known background, and show that motion-blurred ball images, usually unwelcome in computer vision, bear more information than a sharp image. We provide techniques for extracting such information ranging from low-level image processing to 3D reconstruction, and present a number of experiments and possible applications, such as ball localization with speed and direction measurement from a single image, and ball trajectory reconstruction from a single long-exposure photograph.
Paper
Bibtex
@article{caglioti2009recovering,
title={Recovering ball motion from a single motion-blurred image},
author={Caglioti, Vincenzo and Giusti, Alessandro},
journal={Computer Vision and Image Understanding},
volume={113},
number={5},
pages={590--597},
year={2009},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
Estimation of 3D Instantaneous Motion of a Ball from a Single Motion-Blurred Image
Giacomo Boracchi, Vincenzo Caglioti, Alessandro Giusti
Chapter in Book Computer Vision and Computer Graphics. Theory and Applications, 2009
Abstract
We present a single-image algorithm for reconstructing the 3D velocity, the 3D spin axis, and the angular speed of a moving ball. Peculiarity of the proposed algorithm is that this reconstruction is achieved by accurately analyzing the blur produced by the ball motion during the exposure. We combine image analysis techniques in order to obtain 3D estimates, that are then integrated into a geometrical model for recovering the 3D motion.
The algorithm is validated with experiments on both synthetic and camera images. In a broader scenario, we exploit this specic problem for discussing motivations, advantages, and limitations of reconstructing 3D motion from motion blur.
Paper
Bibtex
@incollection{boracchi2009estimation,
title={Estimation of 3d instantaneous motion of a ball from a single motion-blurred image},
author={Boracchi, Giacomo and Caglioti, Vincenzo and Giusti, Alessandro},
booktitle={Computer Vision and Computer Graphics. Theory and Applications},
pages={225--237},
year={2009},
publisher={Springer}
}
Isolating Motion and Color in a Motion Blurred Image
Alessandro Giusti, Vincenzo Caglioti
BMVC 2007
Abstract
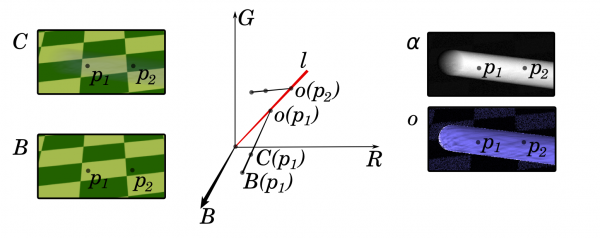
Photographic images of moving objects are often characterized by motion blur; analyzing motion blurred images is problematic since the moving object boundaries appear fuzzy and seamlessly blend with the background. In extreme cases, when the object motion is fast in relation to the exposure time, the blurred object image becomes an elongated, semitransparent smear. We consider a motion-blurred color image of an object moving over a still background: we introduce meaningful entities, the “alpha map” and the “color map”, which bear information about the object motion during the exposure, and its color and texture; we draw connections to the well-known alpha matting problem, providing an original interpretation in this context; we present an analytic technique for extracting the two maps under assumptions on the background and object colors, and explore the relaxation of these assumptions. We provide experimental results on both synthetic and real images, which confirm the correctness of our approach, and describe diverse application examples in fields spanning from 3D reconstruction to image/video enhancement.
Paper
Bibtex
@inproceedings{giusti2007isolating,
title={Isolating Motion and Color in a Motion Blurred Image.},
author={Giusti, Alessandro and Caglioti, Vincenzo},
booktitle={Proc. of BMVC},
year={2007}
}
Basic Video-Surveillance with Low Computational and Power Requirements Using Long-Exposure Frames
Vincenzo Caglioti, Alessandro Giusti
ACIVS 2008
Abstract
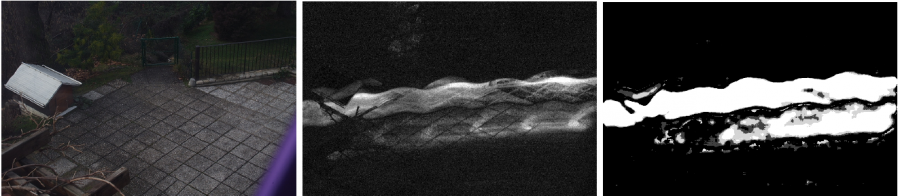
Research in video surveillance is nowadays mainly directed towards improving reliability and gaining deeper levels of scene understanding. On the contrary, we take a di erent route and investigate a novel, unusual approach to a very simple surveillance task (activity detection) in scenarios where computational and energy resources are extremely limited, such as Camera Sensor Networks.
Our proposal is based on shooting long-exposure frames, each covering a long period of time, thus enabling the use of frame rates even one order of magnitude slower than usual, which reduces computational costs by a comparable factor; however, as exposure time is increased, moving objects appear more and more transparent, and eventually become invisible in longer exposures. We investigate the consequent tradeo ff, related algorithms and their experimental results with actual long-exposure images. Finally we discuss advantages (such as its intrinsic ability to deal with low-light conditions) and disadvantages of this approach.
Paper
Bibtex
@inproceedings{caglioti2008basic,
title={Basic Video-Surveillance with Low Computational and Power Requirements Using Long-Exposure Frames},
author={Caglioti, Vincenzo and Giusti, Alessandro},
booktitle={Proc. of Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems},
pages={218--229},
year={2008},
organization={Springer}
}
